Read 18 ~ Socket.io
By Abdallah obaid
| NAME | URL |
|---|---|
| Home | Home. |
| Prep | Prep: Engineering Topics. |
| Read 01 | Node Ecosystem, TDD, CI/CD. |
| Read 02 | Classes, Inheritance, Functional. |
| Read 03 | Data Modeling & NoSQL Databases. |
| Read 04 | Advanced Mongo/Mongoose. |
| Read 05 | Linked Lists. |
| Read 06 | HTTP and REST. |
| Read 07 | Express. |
| Read 08 | Express Routing & Connected API. |
| Read 09 | API Server. |
| Read 10 | Stacks and Queues. |
| Read 11 | Authentication. |
| Read 12 | OAuth. |
| Read 13 | Bearer Authorization. |
| Read 14 | Access Control (ACL). |
| Read 15 | Trees. |
| Read 16 | Event Driven Applications. |
| Read 17 | TCP Servers. |
| Read 18 | Socket.io. |
Socket.io
## WebSocket:
- Its a communication Protocol.
- WebSocket allow the real-time data transfer.
- WebSocket provides bidirectional communication between the Client and the Server over a TCP connection.
- There will be a connection between client and server, the connection will not break after the server returned a response until the client or server do that.
## Socket.io:
- It’s a library.
- It’s wrork a webSocket Protocol.
- It’s divided into two parts:
- Client Side: it is the library that runs inside the browser.
- Server Side: It is the library for Node.js.
- It’s contain additional functionality:
- Broadcasting.
- Namespacing.
- Means of segmenting connected clients into groups. ## difference between Socket.io and TCP connections:
- With TCP, you connect directly to a server with a keep-alive type of connection.
- With Socket.io, you connect to a server over HTTP. The session is “kept alive” through it’s internal use of the WebSocket Protocol, with session information being preserved.
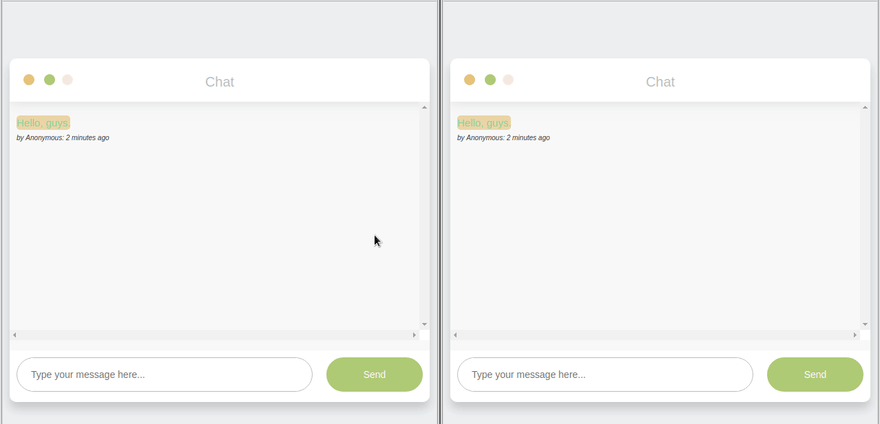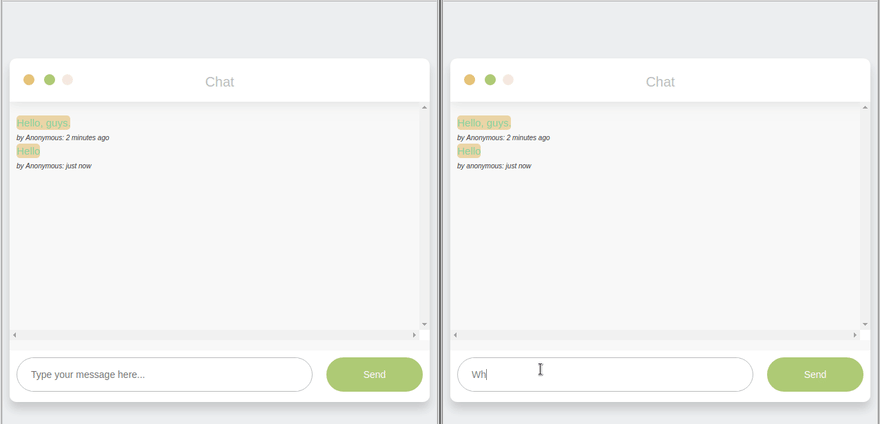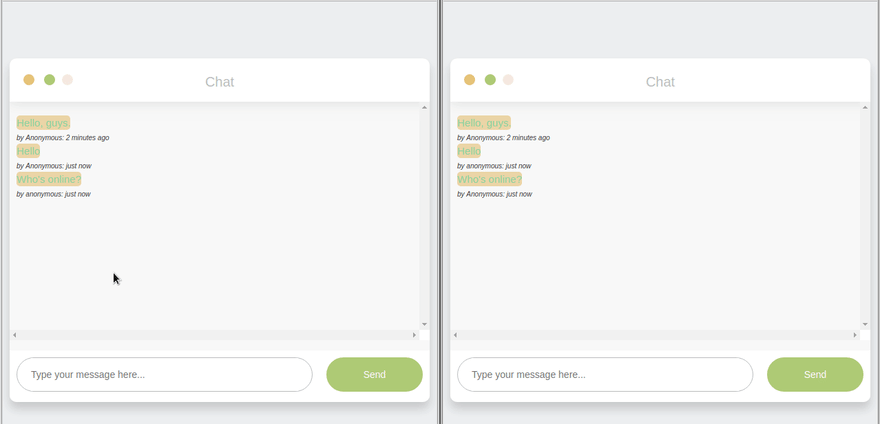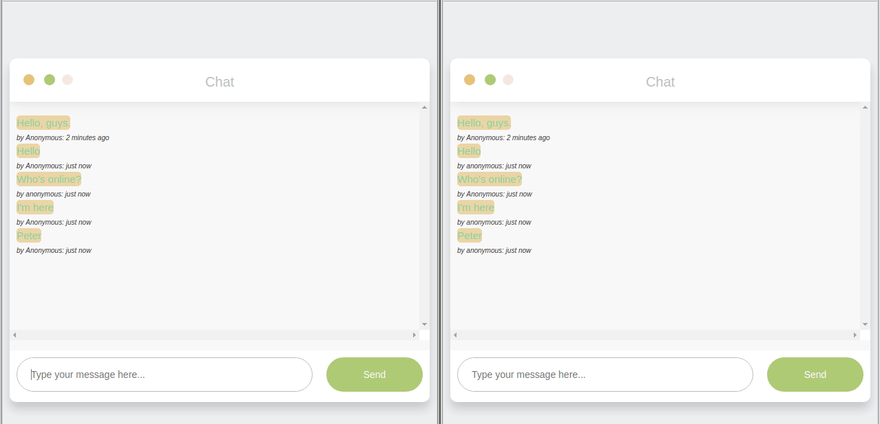
- Socket.io events are sent with emit() and received with on(), events shared between ‘disconnected’ participants. Through a mediator (server), clients connect, emit events, and respond to events from the server.