Read 15 ~ Trees
By Abdallah obaid
| NAME | URL |
|---|---|
| Home | Home. |
| Prep | Prep: Engineering Topics. |
| Read 01 | Node Ecosystem, TDD, CI/CD. |
| Read 02 | Classes, Inheritance, Functional. |
| Read 03 | Data Modeling & NoSQL Databases. |
| Read 04 | Advanced Mongo/Mongoose. |
| Read 05 | Linked Lists. |
| Read 06 | HTTP and REST. |
| Read 07 | Express. |
| Read 08 | Express Routing & Connected API. |
| Read 09 | API Server. |
| Read 10 | Stacks and Queues. |
| Read 11 | Authentication. |
| Read 12 | OAuth. |
| Read 13 | Bearer Authorization. |
| Read 14 | Access Control (ACL). |
| Read 15 | Trees. |
| Read 16 | Event Driven Applications. |
Trees
## Trees:
- A tree data structure can be defined recursively as a collection of nodes (starting at a root node), where each node is a data structure consisting of a value, together with a list of references to nodes (the “children”), with the constraints that no reference is duplicated, and none points to the root.
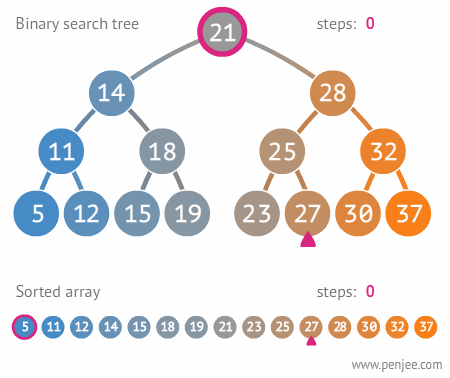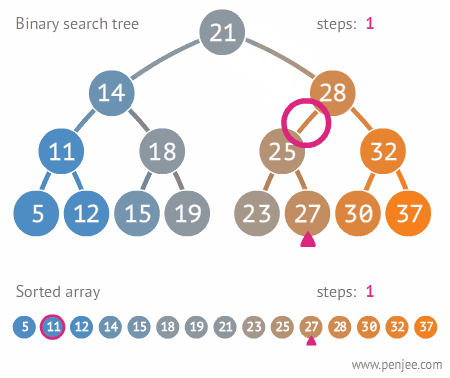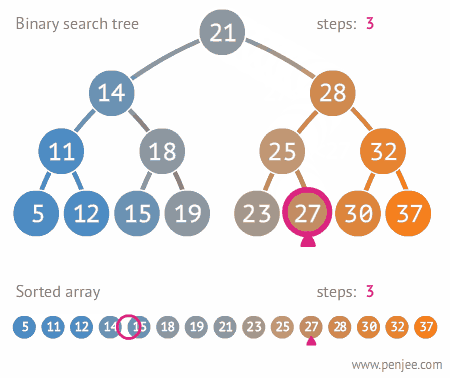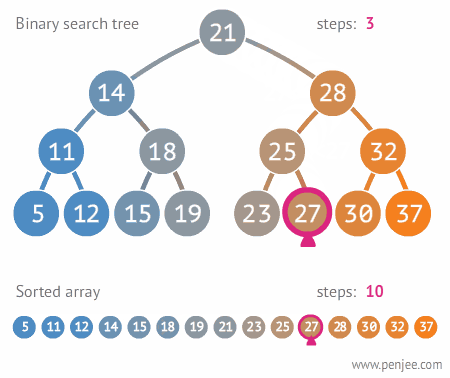
- Trees are good for reducing the search time for an element within the container.
-
Tree: could be traversals by: Depth First Breadth First. - Depth-first divided into three different methods:
- Pre-order: root » left » right
- In-order: left » root » right
- Post-order: left » right » root
- Breadth-first traversal iterates through the tree by going through each level of the tree node-by-node. So, given our starting tree one more time.
## Common Tree Terminology:
- Node - individual item/data that makes up the data structure.
- Root - the first/top Node in the tree.
- Left Child - The node in the left of a root or node.
- Right Child - The node in the right of a root or node.
- Edge - link between a parent and child node.
- Leaf - node that does not contain any children.
- Height - number of edges from the root to the bottommost node
## Binary Tree Data Structure :
- A tree whose elements have at most 2 children is called a binary tree. Since each element in a binary tree can have only 2 children, we typically name them the left and right child.