Read 05 ~ Linked Lists
By Abdallah obaid
| NAME | URL |
|---|---|
| Home | Home. |
| Prep | Prep: Engineering Topics. |
| Read 01 | Node Ecosystem, TDD, CI/CD. |
| Read 02 | Classes, Inheritance, Functional. |
| Read 03 | Data Modeling & NoSQL Databases. |
| Read 04 | Advanced Mongo/Mongoose. |
| Read 05 | Linked Lists. |
| Read 06 | HTTP and REST. |
| Read 07 | Express. |
| Read 08 | Express Routing & Connected API. |
| Read 09 | API Server. |
| Read 10 | Stacks and Queues. |
| Read 11 | Authentication. |
| Read 12 | OAuth. |
| Read 13 | Bearer Authorization. |
| Read 14 | Access Control (ACL). |
| Read 15 | Trees. |
| Read 16 | Event Driven Applications. |
Linked Lists:-
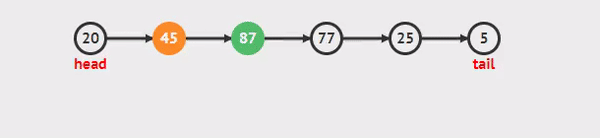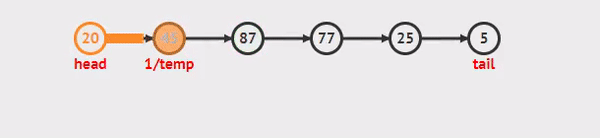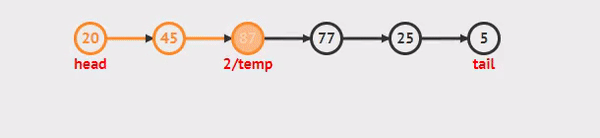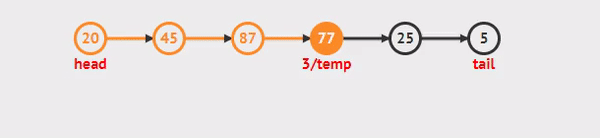
## linked list:
- linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list.
- The linked list could be singly or doubly node reference.
- Singly linked list when the node just refers to the next node.
- Doubly linked list when the node refers to the next and previous node.
- The Next is a property in each node that contains the reference for the next node.
- The Current reference is a reference type of type Node that is currently being looked at.
- The Head is a reference type of type Node to the first node in a linked list.
- We are not able to use a foreach or for loop. We depend on the Next value in each node to guide us where the next reference is pointing.
while()loop Allows us to continually check that the Next node in the list is not null.
## In the Linked Lists we can use:
- Includes.
- Adding (O(1)/middle).
- Print Out Nodes.